Solutions
Horse Construction offers full range of structural strengthening materials with technical supports, documentation supports, products supports, project supports.
1 Minute Understanding Of Prestressed Carbon Fiber Plate Reinforcement
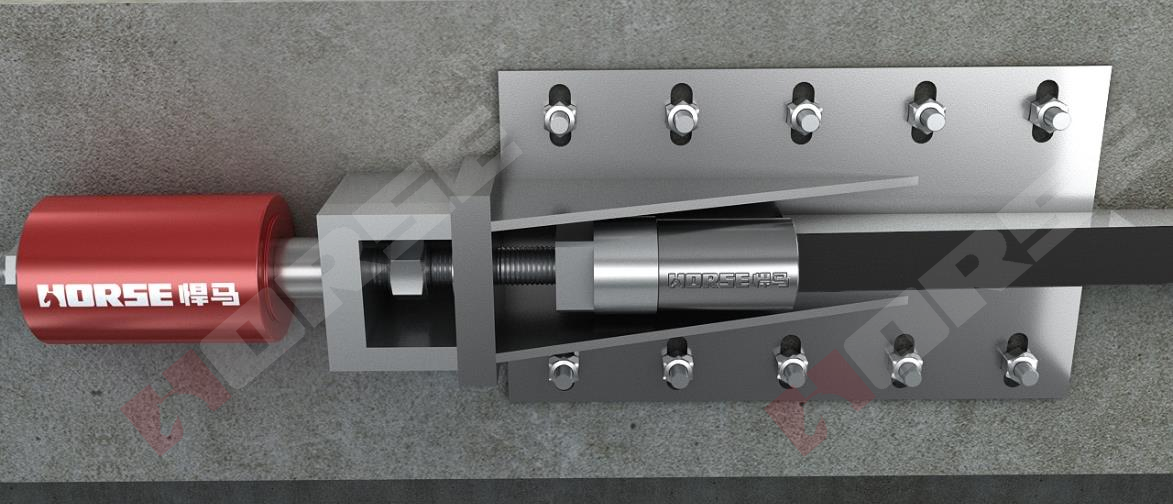

As an efficient reinforcement method for flexural components, prestressed carbon fiber plate has been widely used in industrial and civil buildings, tunnels, bridges, and other fields due to its excellent reinforcement effect, convenient construction process, and durability.
What are the common problems during the tensioning process of prestressed carbon fiber?
Next, a detailed analysis and introduction——
1. Determination of Tensioning Tonnage
The on-site tensioning tonnage should be strictly in accordance with the requirements of the design drawings. The tensioning tonnage is usually determined by the required external pre-stress size of the component, in order to determine the carbon fiber cross-sectional size and tension control stress. The tension control stress of carbon fiber is usually between 600-1400MPa, and this recommended value is clearly specified in GB 50367-2013 "Code for Design of Concrete Structure Reinforcement" and GB 50608-2020 "Technical Standard for Engineering Application of Fiber Reinforced Composite Materials".
2. Dual control of tension tonnage and elongation
To ensure the safety and construction effect of prestressed tensioning, prestressed carbon fiber tensioning is usually carried out using a dual control method of tension and elongation. During tensioning, the carbon fiber shall be tensioned step by step based on the tensioning tonnage and the corresponding elongation shall be recorded. The actual elongation shall be compared with the theoretical elongation, and the deviation shall not exceed 6% and 10%.

3. Calculation of theoretical elongation
Assuming the initial length of carbon fiber is L0, the measured elastic modulus is E, the cross-sectional area is A, and the tension control stress is σ Con, its corresponding tensioning tonnage P and theoretical elongation L should be calculated using the following formula, and attention should be paid to unity of units during calculation.
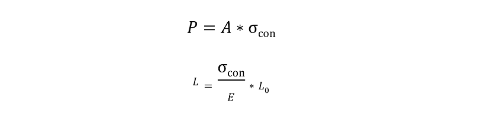
4. Theoretical elongation does not match actual elongation
There is a phenomenon of excessive deviation between the theoretical elongation and the actual elongation during the actual construction process, which includes but is not limited to:
a) The actual elastic modulus of carbon fiber was not used in the calculation
The elastic modulus range of carbon fiber plate/reinforcement for structural reinforcement is usually between 140GPa and 190GPa. The manufacturer should be consulted or the elastic modulus of carbon fibers used in the engineering project should be measured, and the corresponding elongation should be calculated. The calculation should not be based on the elastic modulus value specified in the drawings.
b) Tensioning system issues
During the installation or use of the tensioning anchoring device, there may be significant friction or even locking with the components, which may cause some of the tensioning force to not act on the carbon fiber, resulting in a smaller actual elongation; The slippage between the anchor and carbon fiber or internal components of the anchor can lead to excessive actual elongation.
5. Selection of accessories and tools
The prestressed carbon fiber tensioning accessories mainly include jacks, chemical anchor bolts, compression bars, tensioning screw rods, etc.

a) Jack
The main parameters of prestressed carbon fiber tensioning jack include rated tensioning force, stroke, outer diameter, etc. Generally, the rated tensioning force of the jack should not be less than 1.3 times the design tensioning force. The stroke of the jack is determined by the maximum designed elongation, but depending on site conditions, a small stroke jack can be used for multiple tensioning. The outer diameter of a jack is generally determined by its rated tensioning force, but if conditions permit, it should be ensured that the center of the jack and the height of the tensioning screw are as consistent as possible.
b) Chemical anchor bolt
The number, position, and material of anchor bolts should be determined in accordance with JGJ 145-2013 "Technical Specification for Post Anchorage of Concrete Structures". The commonly used anchor bolt specifications are Grade 5.8 and Grade 8.8. When it comes to anchoring, threaded rods need to be used for anchoring, and their materials should be selected according to JGJ 145-2013 "Technical Specification for Post Anchorage of Concrete Structures".
c) Tensioning screw rod
The tensioning screw rod is an axial tension component, which is generally provided by the anchor manufacturer. When purchasing on site, it should be ensured that its breaking force is more than twice the tension control stress and can withstand the bending effect caused by eccentricity.
You can find anything here you are in need of, have a trust trying on these products, you will find the big difference after that.

Prestressed carbon fiber reinforced polymer(CFRP) strip for slab, beam strengthening to increase stiffness, reduce distortion and deflection of members, reduce the cracks, avoid and stop cracking.

Prestressed carbon fiber reinforced polymer(CFRP) laminate for slab, beam strengthening to increase stiffness, reduce distortion and deflection of members, reduce the cracks, avoid and stop cracking.

Prestressed carbon fiber laminate circular anchorage system includes rigid anchorage, carbon fiber laminate and adhesive, specially designed for bridges, buildings and steel structure reinforcement.